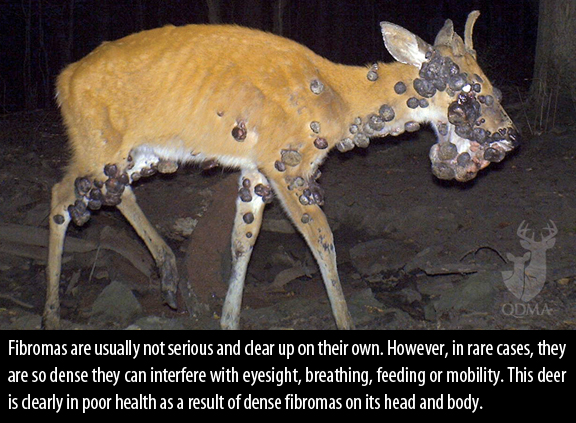
Each year, hunters across the whitetail’s range encounter deer with “warts,” like the buck in the photo above, sent to us by QDMA member Evan Heusinkveld. The growths on these deer are cutaneous fibromas and are caused by a papilloma virus. Cutaneous fibromas are hairless tumors that can be found on any part of the skin, however they rarely extend below the hide. Fibromas are also called warts, tumors, papillomas and fibrosarcomas, and they occur everywhere deer live. They are usually temporary on the body and can vary from 1/2 to 8 inches in diameter, or larger. Fibromas can occur singly or in clumps.
Fibromas are the most conspicuous deer disease, and hunters routinely report them to the state or local deer managers. Fibromas can look grotesque, but unless the tumors become large enough to interfere with an animal’s sight, breathing, eating or walking, they have little impact on the individual animal and thus, little or no impact on the deer population.
Whitetails, blacktails and mule deer can get cutaneous fibromas, which are different from Shope’s fibromas in cottontail rabbits, squirrel fibromas in gray squirrels and woodchucks, and “warts” in livestock. Biting insects and contaminated vegetation can transmit the virus from one deer to another, and an infected deer can transmit the virus by direct contact with another animal. Fortunately deer cannot spread the virus to farm animals or humans.
Should you eat the meat from a deer with fibromas? Only large tumors with secondary bacterial infection cause a deer to be unfit for human consumption. Infected tumors often are swollen and contain yellowish pus. Small, uninfected fibromas like those seen in the photo above do not affect the quality of the meat.
If you see a whitetail with fibromas while hunting, will harvesting that deer prevent the spread of fibromas to other deer? Will it reduce the prevalence of fibromas in your area? Unfortunately, we don’t know the answers to these questions. Given the nature of viral transmission, it is possible that by harvesting that animal, you may prevent the spread of the virus to other deer that animal would have come in contact with. On the other hand, the virus that causes fibromas is present in deer herds across the country, yet it is uncommon and affects only a small percentage of animals. Some deer may even have developed immunity to the virus. And, for most deer, fibromas are harmless, and the individual will eventually recover. For these reasons, harvesting a deer just because it has fibromas is probably not necessary unless the animal has an extremely severe case and is clearly debilitated.